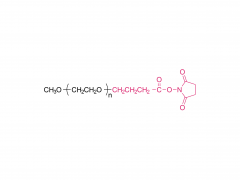
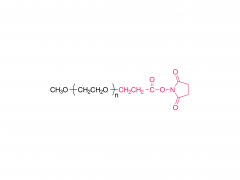
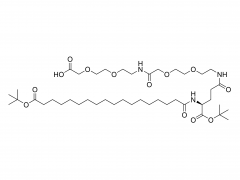
A Y-shaped polyethylene glycol derivative is a specially structured polymer with a Y-shaped molecular structure. It is formed by connecting the centroids of three polyethylene glycol (PEG) units, where two PEG chains are connected to the two ends of the centroid and the third PEG chain is connected to the middle of the centroid.
The advantages of Y-shaped polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives include:
Increased Stability: Y-shaped PEG derivatives provide improved stability compared to linear PEG, which can lead to enhanced performance and efficacy in various applications.
Enhanced Targeting: The unique structure of Y-shaped PEG derivatives can offer better targeting capabilities, allowing for more precise delivery of drugs or other substances to specific sites within the body.
Improved Solubility: Y-shaped PEG derivatives often exhibit superior solubility properties, which can enhance the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs and increase their effectiveness.
Reduced Immunogenicity: Y-shaped PEG derivatives tend to have lower immunogenicity compared to other polymers, making them a more attractive option for biomedical applications.
Versatile Functionalization: Y-shaped PEG derivatives can be easily functionalized with various molecules, enabling the creation of tailor-made compounds for specific therapeutic purposes.
Extended Circulation Time: Y-shaped PEG derivatives have been shown to prolong the circulation time of drugs in the body, leading to a sustained release effect and potentially reducing the frequency of dosing.
Overall, Y-shaped PEG derivatives offer a promising platform for drug delivery systems and other biomedical applications due to their unique properties and benefits.