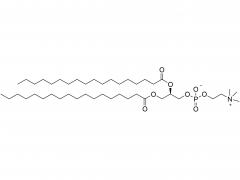
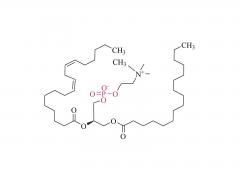
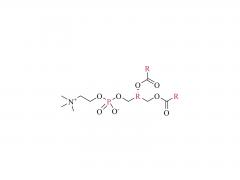
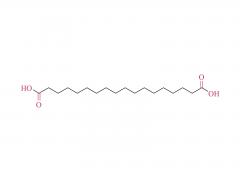
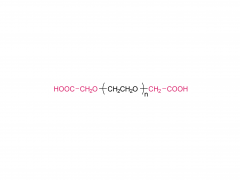
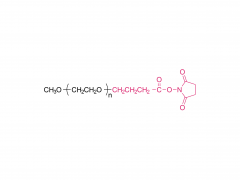
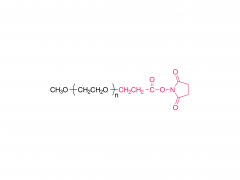
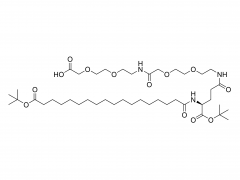
Drug delivery is an important issue in modern medicine, and the selection of suitable drug carriers can effectively enhance drug solubility, prolong in vivo circulation time, enhance drug efficacy, and reduce side effects. A common drug delivery strategy is to usezwitterionicblock copolymers containing amphiphilic units to form micelles with a core-shell structure by self-assembly, and then encapsulate the drug in its hydrophobic core, such as the common anticancer drug adriamycin (DOX). Also, drug delivery systems based onzwitterionicpolymers can be applied to the delivery of nucleic acid drugs. In addition,zwitterionicpolymers can also be used to construct other structural drug delivery systems: Wu and Cheng at the State University of New York at Buffalo have synthesized a biodegradable poly(lactic acid) (PLA) backbone and synthesized PLA-SB/PTX as a coupling between the anticancer drug paclitaxel (PTX) andzwitterionicpolymers, which can release PTX through biodegradation to kill tumor cells. This coupling can release PTX through biodegradation to kill tumor cells and achieve anti-cancer; Shengfu Chen et al. of Zhejiang University prepared anzwitterionicpolymer hydrogel with triple responsiveness of ionic strength, pH and enzyme using polyamino acid as the backbone, which is expected to achieve targeted release of drugs.