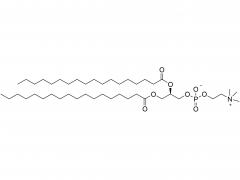
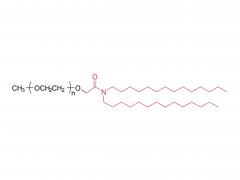
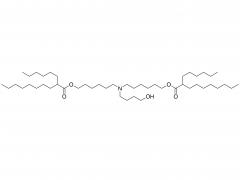
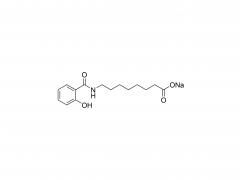
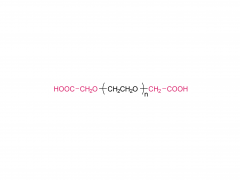
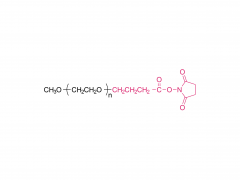
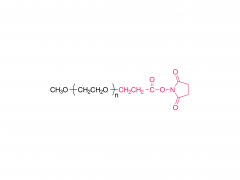
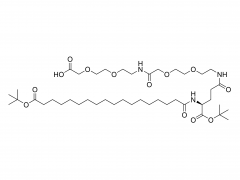
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) is a polymer widely used in chemical and biomedical fields. The PEG structural unit is a linear polymer generated by repeated ethylene oxide (EO) ring-opening polymerization reactions of ethylene glycol (EG) with two hydrogen atoms bridged by oxygen atoms.
The structure of PEG can be expressed as (-CH2CH2O-)n, where "n" represents the number of monomer units, namely the polymerization degree. The polymerization degree varies widely from low molecular weight to high molecular weight, which makes PEG have a variety of physical and chemical properties, such as solubility, viscosity, hygroscopicity and surface activity, to meet the needs of different fields.
Each segment of PEG contains a hydrophilic hydroxyl group (-OH), which gives it good water solubility and biocompatibility, making it an important component of drug carriers, biomarker reagents, cosmetic additives and many medical and industrial products.
In addition, the end of PEG can be modified by a variety of chemicals, such as esterification, amine, acylation, etc., forming a series of derivatives, further broadening its application in drug controlled release systems, protein and nucleic acid modification, tissue engineering scaffold materials and so on.
In the field of medicine, PEG is widely used in drug delivery systems. Due to its good biocompatibility and adjustable molecular size, polyethylene glycol can be used as a drug carrier to help drugs be better delivered to target cells, improve drug efficacy and reduce toxic side effects. Polyethylene glycol-modified drug nanoparticles and microspheres are also commonly used for controlled release drugs to prolong the action time of drugs and improve therapeutic effects. In the field of chemical industry, polyethylene glycol is an excellent thickener and lubricant. Due to its high solubility and low viscosity, polyethylene glycol is often used to prepare various liquid products, such as detergents, lubricants and softeners. In addition, polyethylene glycol can also be used for the synthesis of polymer materials, such as polyether alcohol and polyurethane, which have wide applications in the plastic industry and adhesives. In the food industry, polyethylene glycol is also used as a food additive. Due to its non-toxic, tasteless and easy to dissolve, polyethylene glycol is often added to food as a thickener, anti-caking agent or humectant to improve the taste and texture of food and extend the shelf life of food.
As a multi-functional polymer material, polyethylene glycol has important application value in medicine, chemical industry, food and other fields. With the continuous development of science and technology, it is believed that the application of polyethylene glycol in more fields will continue to expand, and make greater contributions to the development of human society.