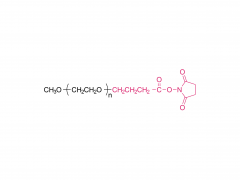
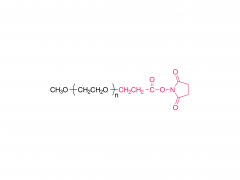
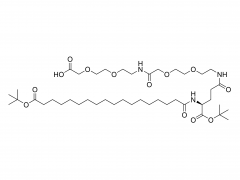
As a widely used polymer material, polyethylene glycol has important value in medicine, cosmetics, chemical industry and other fields. Its unique properties and functions are closely related to its molecular weight, so understanding and mastering the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is the basis for in-depth exploration of its characteristics and applications.
Polyethylene glycol is a linear polymer generated by ring-opening polymerization of ethylene oxide. Its molecular weight range is wide, ranging from hundreds to millions of daltons. According to the different molecular weights, polyethylene glycol can present different physicochemical properties and biological activities. Low molecular weight polyethylene glycol is usually used as a solvent, wetting agent or dispersant, with good water solubility and permeability; with the increase of molecular weight, its viscosity, melting point and metabolism rate in the body will change significantly. High molecular weight polyethylene glycol is more widely used in drug sustained release systems, tissue engineering scaffold materials and various industrial formulations.
The molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is particularly critical for its application in pharmaceutical preparations. The application in pharmaceutical preparations is rich in diversity due to its different molecular weights, with their own characteristics and advantages.
Applications of low molecular weight polyethylene glycol: low molecular weight polyethylene glycol is usually referred to as MW.
Applications of medium molecular weight polyethylene glycol: Medium molecular weight polyethylene glycol (usually between 2000 and 30000 Da) is mainly used in the preparation of solid dispersions or microcapsule systems in the field of pharmaceutical preparation. By wrapping the drug in the polymer matrix formed by PEG, the original physical state of the drug can be changed, the dissolution rate of the drug can be increased, and the rapid absorption and onset can be achieved.At the same time, this form of encapsulation can achieve targeted delivery of drugs, that is, the release of drugs can be controlled at specific sites to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. For example, in anti-tumor drugs, the use of medium molecular weight polyethylene glycol can design intelligent nanocarriers that can selectively release drugs in tumor tissue.
Applications of high molecular weight polyethylene glycol: High molecular weight polyethylene glycol (MW>30000 Da) is often used as a drug excipient for the development of long-acting preparations.This kind of macromolecular PEG can delay the release rate of drugs from the preparation, providing a sustained and stable blood drug concentration to meet the needs of long-term treatment. In oral administration, high molecular weight polyethylene glycol can achieve long-term effects by regulating the absorption of drugs in the intestine; in topical administration such as ophthalmology and dermatology, it helps to extend the time of action of drugs in the local area; In the injection administration, it can be used as a drug carrier, made into microspheres, gels or other sustained-release structures, to ensure the slow release of drugs in the body, reduce the burden of frequent administration, and maintain a stable therapeutic effect.
In general, the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol not only determines its basic physicochemical properties, but also directly affects its practical application in various fields. By precisely regulating the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol, we can customized design products to meet specific needs, thereby broadening its application prospects in science and technology, medicine and daily life.