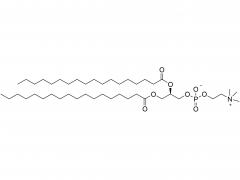
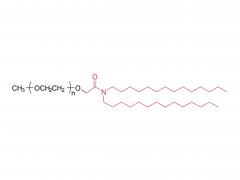
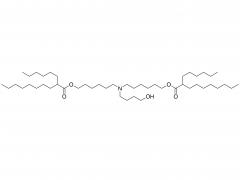
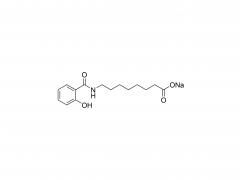
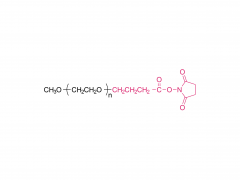
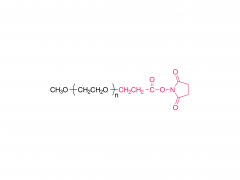
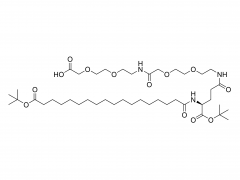
Join Us at CPHI China 2025! SINOPEG's booth no. W4F66 Exciting news! CPHI China 2025 is just around the corner, taking place June 24–26 at the Shanghai New International Expo Centre. SINOPEG will be showcasing cutting-edge drug delivery system (DDS) solutions at Booth W4F66. As your trusted partner in specialty chemicals and advanced drug delivery systems, we’re eager to share innovations that drive industry progress. Why visit us? Explore our latest portfolio of PEG derivatives, lipids, and custom synthesis services Discuss tailored solutions for your R&D and manufacturing challenges Connect face-to-face with our technical experts We warmly welcome friends, partners, and industry peers from around the globe to drop by! Let’s collaborate to shape the future of pharma. Dates: June 24–26, 2025 Venue: Shanghai New International Expo Centre Our Booth: W4F66 (Hall W4) Ready to meet? Simply stop by!
View More