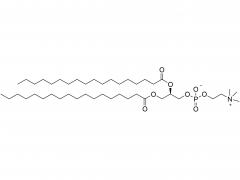
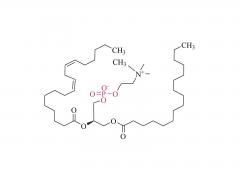
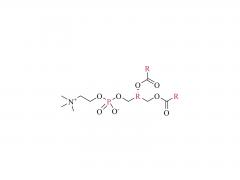
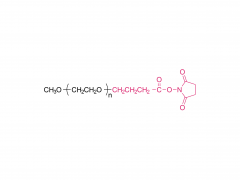
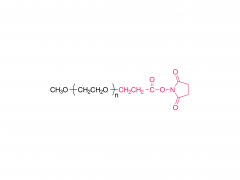
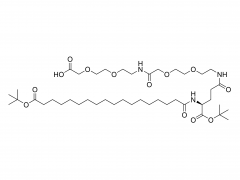
DLin-MC3-DMA (1,2-dilinoleyloxy-3-dimethylaminopropane) is a synthetic lipid commonly used in the preparation of nanoparticles, particularly in gene and drug delivery systems.
DLin-MC3-DMA belongs to the category of ionizable amphiphilic lipids, with a structure containing a positively charged amino group and two lipophilic chains. This allows DLin-MC3-DMA to form stable nanoparticles or liposomes with negatively charged nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. These nanoparticles can be utilized for gene delivery or gene therapy, enabling the transport of exogenous genetic materials into cells to achieve gene expression or repair defective genes.
The mechanism of action of DLin-MC3-DMA primarily involves the protection of nucleic acids through charge interactions and the stability of the lipid bilayer, enhancing the cellular uptake efficiency of nucleic acids. Additionally, DLin-MC3-DMA can also modify the membrane permeability of cells to facilitate the uptake of nanoparticles.
It is important to note that the specific applications and performance of DLin-MC3-DMA as a lipid material are influenced by other factors such as the type of loaded nucleic acids, the size of nanoparticles, and surface modifications. Therefore, a comprehensive consideration of these factors is required when evaluating the effects and functionality of DLin-MC3-DMA in specific applications.