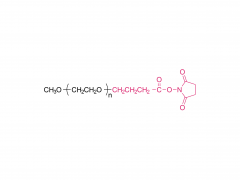
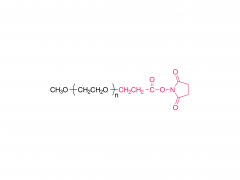
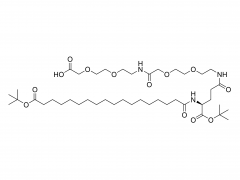
Amino polyethylene glycol, as an important biomedical material and chemical synthesis reagent, has wide application value in drug delivery systems, protein modification, nanomaterial preparation, and biosensors.
Amino polyethylene glycol is a derivative of linear polyethylene glycol (PEG) obtained by introducing amino functional groups at its end through specific chemical reactions.The core structure of PEG has good water solubility, low toxicity, non-immunogenicity, and biocompatibility, while the amino group at the end gives it more chemical activity, making it easy to couple or modify with other molecules, greatly expanding its application potential in the field of biomedicine.
In drug delivery, amino polyethylene glycol is used to improve the water solubility, stability, and blood circulation time of drug molecules, thereby improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects.By covalently combining with drug molecules to form "PEG-modified" drugs, it can effectively avoid rapid metabolic clearance of drugs and prolong the action time of drugs.
In protein engineering, amino polyethylene glycol is often used as a protein surface modifier. By reacting with the side chain or N-terminal and C-terminal amino acid residues of proteins, it can regulate the physicochemical properties of proteins, such as solubility, stability and immunogenicity, which is of great significance for improving the pharmacokinetic properties of protein drugs.
In addition, amino polyethylene glycol has been particularly significant in nanotechnology and materials science, especially in the surface functionalization modification of nanomaterials. By combining amino polyethylene glycol to the surface of nanoparticles, the physicochemical properties of nanoparticles can be effectively regulated, such as changing the surface charge distribution from hydrophilic or hydrophobic to a specific hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance. This transition is crucial for the stability, dispersibility and cell uptake rate of nanoparticles in the biological environment.
Because of the good biocompatibility and immunogenicity of PEG chain, amino polyethylene glycol-modified nanoparticles can effectively reduce non-specific protein adsorption, prolong blood circulation time, and improve targeting efficiency. This plays a decisive role in the design of precision drug delivery systems, the realization of long-term circulation of drugs in the body and selective enrichment of tumor sites, as well as the reduction of toxic side effects.
At the same time, in the field of biological imaging, upconversion nanoparticles, quantum dots and other fluorescent nanoparticles wrapped in amino polyethylene glycol have become ideal tools for real-time and high-sensitivity imaging in vivo due to their excellent optical properties and biological safety. These nanoparticles, after PEG-NH2 modification, can improve the penetration and retention time in biological tissues while maintaining their excitation and emission spectral characteristics.
In biosensing and diagnostic technology, amino polyethylene glycol nanoplatforms also show great potential. They can serve as carriers for molecular recognition elements, identify molecules by covalently connecting antibodies, nucleic acid aptamers or other biomarkers, enhance the signal amplification effect, and thus improve detection sensitivity and specificity.
In recent years, with the continuous progress of scientific research technology, the research and application of amino polyethylene glycol have shown a trend of more diversification and refinement, providing new ideas and technical means for new drug design, biological material research and development, and precision medicine. In the future, amino polyethylene glycol is expected to play a key role in more frontier scientific fields, and further promote the progress and development of relevant scientific research and industry.